Using Multiple Authentication Methods for Kibana
In some cases you might need to offer more than one authentication method to the users which access your Kibana installation.
There are two approaches to this:
- Search Guard displays a list of available authentication methods on the login page. The user can then choose the appropriate login method.
- You run several Kibana instances, each configured with a different login method. Users which open the URL of the respective Kibana instance in their browser, will be automatically presented with the configured login method.
Several Authentication Methods in one Kibana Instance
Configuring more than one authentication method for Kibana is straight forward: The sg_frontend_authc.yml configuration allows to configure more than one login method at once.
This might then look like this:
default:
auth_domains:
- type: basic
- type: saml
label: "SAML Login"
saml.idp.metadata_url: "http://your.idp/auth/realms/master/protocol/saml/descriptor"
saml.idp.entity_id: "IdP entity id from the IdP"
saml.sp.entity_id: "SP entity id from the IdP"
The resulting login screen will then look like this:
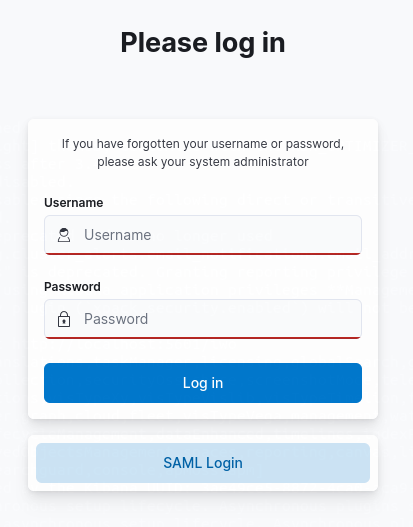
You can also configure several auth_domains entries using the same type. So, you can support several IdPs at once. Use the label attribute of each entry to give the user a short hint what authentication method is configured here. The value of the label attribute will be displayed on the button that links to the IdP.
Setting a default authentication method
Introduced in Search Guard FLX 1.2
If you have multiple authentication methods and you want to designate one of them as the default method presented to users, you can use the auto_select: true property.
This feature is useful when you have a preferred authentication method that should be used most of the time, but you still want to keep others as fallback or emergency options.
To configure the default authentication method, include auto_select: true property to your method in sg_frontend_authc.yml as in this example:
default:
auth_domains:
- type: basic
- type: saml
label: "SAML Login"
auto_select: true
saml.idp.metadata_url: "http://your.idp/auth/realms/master/protocol/saml/descriptor"
saml.idp.entity_id: "IdP entity id from the IdP"
saml.sp.entity_id: "SP entity id from the IdP"
- type: "oidc"
id: "oidc_optional"
label: "OIDC Login"
oidc.client_id: "Client id from the IdP"
oidc.client_secret: "Client secret from the IdP"
oidc.idp.openid_configuration_url: "http://your.id/realms/master/.well-known/openid-configuration"
user_mapping.roles.from: "oidc_id_token.roles"
When an unauthenticated user enters Kibana or logs out, they will be automatically redirected to SAML login.
All other methods can be still visible if a user enters /login page. They can also be accessed with their respective URLs by id. In our example: /auth/oidc/login?authTypeId=oidc_optional.
Only one endpoint per instance can be marked with auto_select: true.
Direct access to the authentication method
Search Guard provides a number of defined endpoints to directly access individual authentication methods. You can use these endpoints to override the auto_select setting or to skip the standard login page.
The endpoints are the following:
basicauthentication:https://your-kibana-instance/loginon Elasticsearch 7.x andhttps://your-kibana-instance/searchguard/loginon Elasticsearch 8.x. Note: This also includes links to other auth methods if configured.samlauthentication:https://your-kibana-instance/auth/saml/login. If you have more than one SAMLauth_domainconfigured, you need to give each auth domain an explicit ID (see below) and reference that in the endpoint withhttps://your-kibana-instance/auth/saml/login?authTypeId={id}.oidcauthentication:https://your-kibana-instance/auth/oidc/login. If you have more than one OIDCauth_domainconfigured, you need to give each auth domain an explicit ID (see below) and reference that in the endpoint withhttps://your-kibana-instance/auth/oidc/login?authTypeId={id}.
Giving an authentication method an explicit ID
In the case that you are using several auth domains with the same type, you need to identify each auth domain with an explicit ID in order to reference it using one of the links described above. Use the id attribute for this. This might look like this:
default:
auth_domains:
- type: basic
- type: saml
id: your_saml_idp_1
label: "SAML Login"
saml.idp.metadata_url: "http://your.idp/auth/realms/master/protocol/saml/descriptor"
saml.idp.entity_id: "IdP entity id from the IdP"
saml.sp.entity_id: "SP entity id from the IdP"
- type: saml
id: your_saml_idp_2
label: "SAML Login"
saml.idp.metadata_url: "http://your.other.idp/auth/realms/master/protocol/saml/descriptor"
saml.idp.entity_id: "IdP entity id from the IdP"
saml.sp.entity_id: "SP entity id from the IdP"
Now the two methods can be accessed with /auth/saml/login?authTypeId=your_saml_idp_1, respectively /auth/saml/login?authTypeId=your_saml_idp_2.
When id is not provided, the domain will receive a hashed hex value (like ed017b18). This value may be regenerated during configuration change, so do not leave id blank if you wish to provide users with a consistent URL to your method.
Running Several Kibana Instances
If you are running several instances of Kibana, you can assign each Kibana instance a different authentication configuration.
To achieve this, the sg_frontend_authc.yml configuration file allows you to specify additional configuration entries, besides the usually existing default entry.
So, you can have your sg_frontend_authc.yml like this:
default:
auth_domains:
- type: basic
another_instance:
auth_domains:
- type: saml
idp.metadata_url: "http://your.idp/auth/realms/master/protocol/saml/descriptor"
idp.entity_id: "IdP entity id from the IdP"
sp.entity_id: "SP entity id from the IdP"
roles_key: "roles"
On the Kibana instance, which is supposed to use SAML authentication, edit the file config/kibana.yml and add this line:
searchguard.sg_frontend_config_id: another_instance
This makes the Kibana instance use the configuration entry another_instance in sg_frontend_authc.yml.
In order to activate the changes, do not forget to upload sg_frontend_authc.yml and restart the particular Kibana instance afterwards.